Experts warn AI could wipe out thousands of voice acting jobs.
Industry leaders say the rise of AI-generated voices is reshaping creative fields at an alarming rate. In Australia, actors and unions fear that affordable AI voice clones could replace up to 5,000 jobs.
The concern is spreading across industries, from gaming to advertising, as businesses opt for synthetic voices that are faster, cheaper, and increasingly difficult to distinguish from human speech.
But is this a total takeover or a transformation?
As AI-generated voices become nearly indistinguishable from human speech, we dug into the numbers to find out what’s really happening. Is voice acting on the verge of collapse, or is there a future where AI and human voices coexist?
The truth might surprise you.
KEY FINDINGS
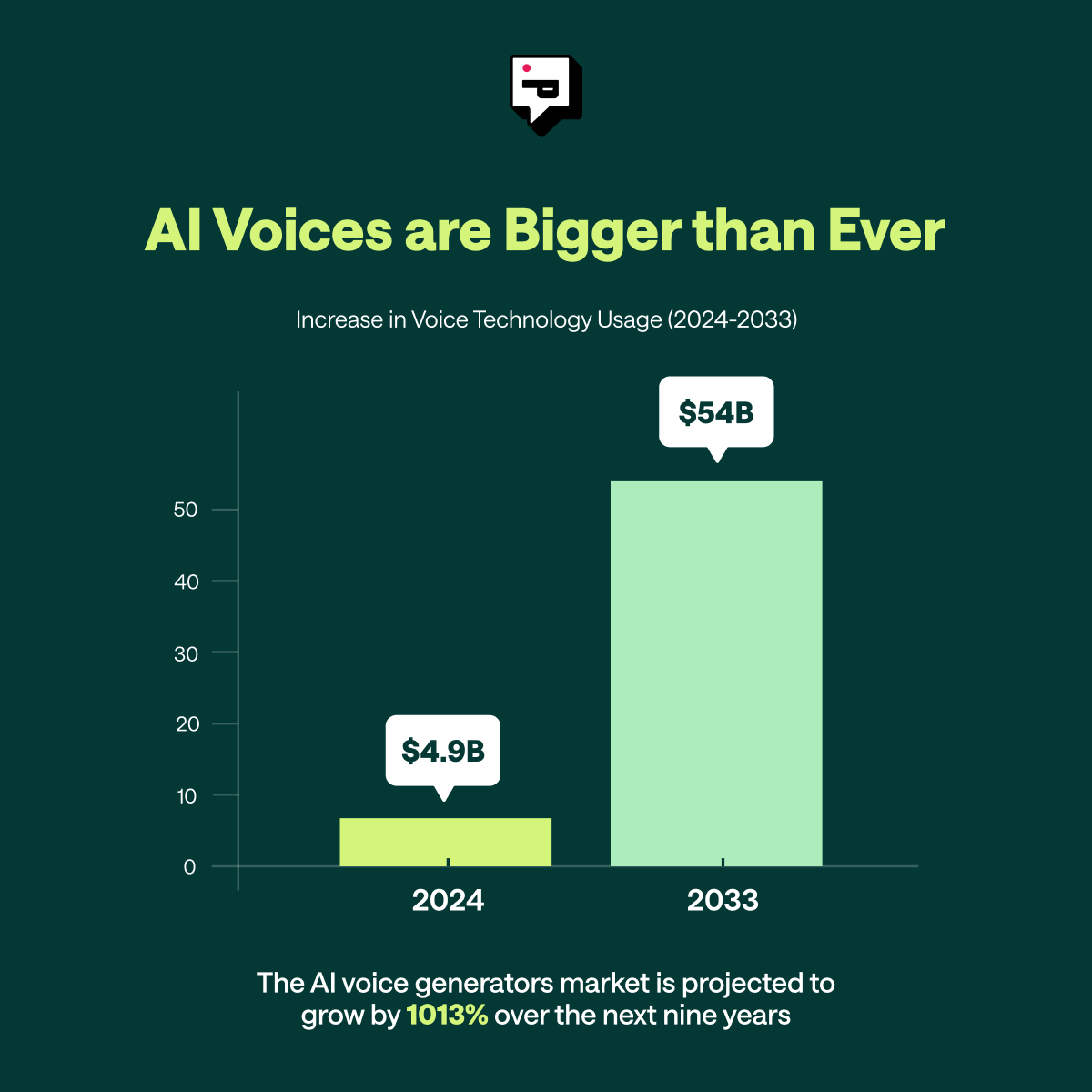
- The AI voice generator market is projected to grow from $4.9 billion in 2024 to $54 billion by 2033, highlighting massive industry expansion.
- 82% of companies are using AI voice technology in some capacity, according to a 2023 Deepgram report.
- A Podcastle test found that AI-generated voiceovers completed 30 narrated blog summaries before a freelancer could provide a quote, showcasing AI’s speed advantage.
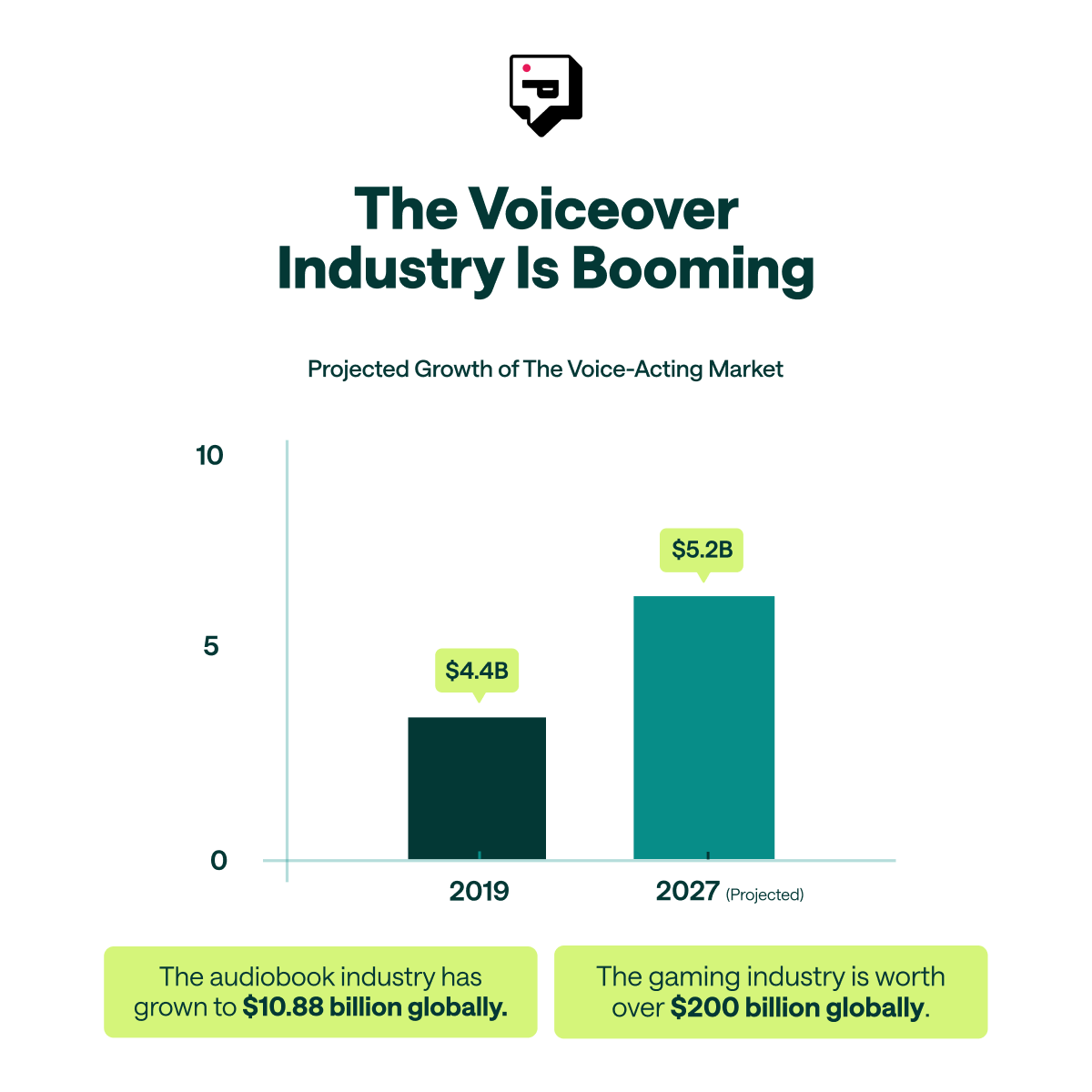
- Despite AI’s rise, the global audiobook market is expected to grow from $10.88 billion in 2025 to $56 billion by 2032, proving demand for voice content is increasing.
- The gaming industry is projected to exceed $200 billion, fueling investment in professional voice actors for immersive storytelling.
- 63% of Americans struggle to differentiate AI voices from real human speech, making synthetic voices increasingly indistinguishable.
- A Voices.com survey found that 37.8% of voice actors were booked for “real person” roles, proving that human authenticity remains in high demand.
- 93% of brands say that social media videos play a key role in customer acquisition, driving demand for both AI and human voiceovers in content creation.
Table of Contents
1. The Rise of AI Voiceovers
2. The Impact on the Voiceover Industry
3. The Most In-Demand AI Voices and Accents
4. How Do AI Voices Work?
5. How to Tell AI Voices and Human Speech Apart
6. The Ethics of AI Voices and Voice Cloning
7. How Clients Choose Voiceover Artists
8. The Future of AI and Human Voiceovers
9. How To Create Content with AI Voices
10. Where Do We Go From Here?



The Rise of AI Voiceovers
AI-generated voices are everywhere, and they’re only getting better. Companies are using them for marketing, content creation, customer service, and internal training. This rapid adoption is why scaling voice-based content faster and cheaper than ever before. And investment and adoption are reaching unprecedented levels with the AI voice generator market projected to surge from $4.9 billion in 2024 to $54 billion by 2033.
The Big Players: Who’s Driving AI Voice Innovation?
The explosion of AI voice technology is no accident. Leading companies are pouring millions into research and development, refining voice synthesis to be more realistic and versatile.
ElevenLabs, one of the most well-known names in the AI voice industry, recently secured $180 million in Series C funding. Meanwhile, other leading industry players like Podcastle have rapidly expanded AI voice capabilities. Following their Series A funding round at the beginning of 2024, the company focused on pushing AI voice synthesis forward, developing an extensive library of over 1000 hyper-realistic AI voices that surpass existing alternatives in authenticity and range.
With AI voices improving at an extraordinary pace, it’s no surprise that enterprise adoption is accelerating. A 2023 Deepgram report surveying over 400 business leaders found that 82% of companies are using voice technology in one way or another. Businesses are integrating AI-generated voices across industries, not just for efficiency but as a fundamental tool for scaling content production. And the numbers are only expected to go up.
Why Companies Choose AI Over Voice Actors
Businesses today operate at a speed that traditional voiceover workflows struggle to keep up with. Hiring a professional voice actor requires multiple steps: sourcing talent, negotiating rates, scheduling recording sessions, and waiting for revisions. Even for a short project, this process can take days—if not weeks—to finalize. AI-generated voices eliminate these bottlenecks entirely.
For many companies, cost alone is the deciding factor. A single professional voiceover can cost anywhere from $500 to $2,000, depending on the complexity and licensing requirements. AI voice platforms, on the other hand, provide unlimited voice generation for a fraction of the price through affordable subscription models. This makes AI particularly appealing for businesses producing large volumes of content, such as corporate training videos, product explainers, and social media ads.
AI-generated voices also offer immediate scalability. Once a voice is trained or selected, it can generate hours of narration in minutes without the need for reshoots, retakes, or additional costs. This level of speed and flexibility allows companies to adapt content quickly and for any communication channel.
This realism, combined with accessibility and cost-effectiveness, explains why companies are increasingly favoring AI voices for practical applications.
Can You Spot the Difference?
We've put together two different adreads. Which one sounds like AI to you? (If you want to check if you're right, the answer is near the bottom of this page.)
AI vs VA: A Real Test Conducted at Podcastle
To measure just how much AI voices can accelerate production, Podcastle conducted an internal test. A content strategist was tasked with generating blog summaries using Podcastle’s AI voice technology, while another team member attempted to commission a human voiceover artist through Fiverr.
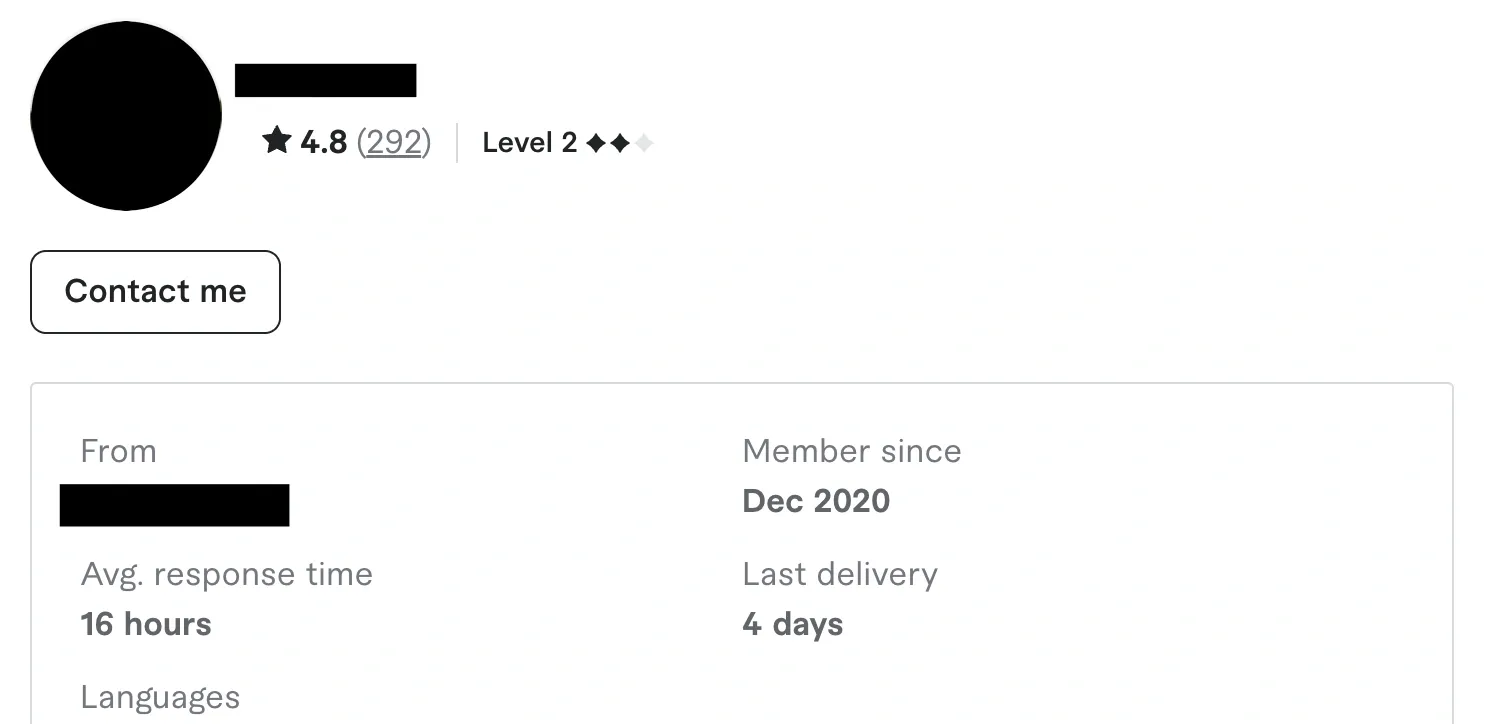
The freelancer’s listing stated a 16-hour response time for initial contact. By the time they replied with a quote, the Podcastle strategist had already generated 30 fully narrated blog summaries using AI voices and ChatGPT, including the one for this article. Before the freelancer could reply with pricing and estimated turnaround times, the AI-generated content was completed, revised, and ready for distribution.
While there were a handful of voiceover artists with an average response rate of one hour, their estimated turnaround time for delivering the final work was two to three days.
This real-world test highlights why AI voices are becoming the go-to solution for fast-paced content creation. The ability to generate, edit, and finalize voiceovers instantly provides businesses with a level of agility that traditional voiceover processes can’t match.
As AI voice technology continues to evolve, its role in content production will only expand and scale content in ways that were never possible before.
The Impact on the Voiceover Industry
AI-generated voices have shaken up the voiceover industry, sparking concern about the future of human voice actors. Some believe AI is making traditional voice work obsolete, while others argue it’s simply shifting where professional voice actors are needed.
The reality is far more nuanced.
Why Demand for Voiceover Is Stronger Than Ever
Despite the rise of AI voices, the demand for voiceover talent has never been higher. The explosion of digital content has expanded the industry, creating more opportunities across gaming, social media, audiobooks, and podcasting.
In 2025, Spotify is estimated to have over 6 million podcasts, 250,000 video podcasts, and 350,000 audiobooks. The global podcasting market is expected to grow at a 27.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2023 to 2030, showing no signs of slowing down. Similarly, the audiobook industry has grown to $10.88 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach $56 billion by 2032, as more consumers opt for audio content over traditional reading.
Gaming is another major force in voiceover demand. With the gaming industry projected to exceed $200 billion, studios are investing more in professional voice talent for immersive storytelling. Games that rely on strong character performances are seeing increased budgets for voiceover work, as players expect cinematic-quality dialogue and dynamic, interactive experiences.
Social media platforms have further amplified the importance of voiceover as well, with 93% of brands reporting that social media videos across platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram have played a role in acquiring new customers.
The shift in digital consumption means voice acting remains essential, but the type of voice work in demand is changing. AI-generated voices have gained ground in some areas, while human voice actors are finding new opportunities in others.
Where AI is Replacing Traditional Voice Acting
AI-generated voices are increasingly being used for functional, high-volume voice work that prioritizes efficiency over creative performance. Businesses producing corporate training materials, internal communications, explainer videos, and AI-generated assistants are opting for synthetic voices to cut costs and speed up production.
Some voice actors, like Jordan Fritz from Australia, have already seen a drop in small-scale YouTube and e-learning opportunities:
"Over the last probably six months to 12 months, I've seen like a 90 per cent drop in those smaller jobs like the YouTube channels.
Even one of the bigger companies I work for mentioned that they had toyed with the idea of basically recording their original recording and then using AI to shift it to an Australian accent.”
Social media content is another major area where AI voiceovers have taken hold. Brands and content creators frequently use text-to-speech AI voices to narrate short-form videos, particularly when content needs to be produced quickly.
For entry-level voiceover artists, these changes are significant. Many of the smaller projects that once served as stepping stones into the industry, such as low-budget YouTube videos, e-learning modules, and voicemail recordings, are now being handled by AI. This has reduced the number of beginner-friendly opportunities available for aspiring voice actors.
Where Human Voice Actors Are Thriving
Despite AI’s explosive rise, human voice actors remain the preferred choice for specific types of roles. A recent survey by Voices, one of the biggest voiceover freelancing platforms, found that:
- 37.8% of voice actors were booked for “real person” roles that required natural, authentic delivery.
- 23.2% worked on narration projects.
- 12.1% specialized in character-driven performances for animation, gaming, or film.
- 8.6% were hired for announcer-style voiceovers.
- 7.8% focused on instructional content like corporate training and e-learning.
Whereas the most requested voiceover styles reflected a shift toward natural, conversational delivery over traditional announcer reads:
- Conversational read (most popular)
- Believable read – 14.1%
- Genuine read – 11.7%
- Informative read – 10.2%
- Sincere read – 8.8%
- Engaging read – 6.4%
This is why the biggest voiceover markets, namely podcasting, gaming, audiobooks, animation, and high-end commercial work, still thrive for voiceover artists. The demand for human voice acting isn’t disappearing. It’s being refocused on roles requiring emotion, creativity, and flexibility, areas where AI struggles no matter how advanced.
The Most In-Demand AI Voices and Accents
As AI-generated voices become more advanced, demand for specific accents and celebrity voice clones is increasing. Everyone is searching for voices that enhance branding, localization, and engagement. The most requested AI voices reflect these priorities, shaping how synthetic speech is used across industries.
The Most Popular AI Voice Accents - AHrefs Data
Different regions and industries favor particular accents for AI-generated voices. British, Scottish, and Australian AI voices are among the most searched, likely due to their association with authority, sophistication, and global appeal in media and advertising.
The patterns in voice preference reveal a lot about what audiences connect with. Some accents naturally dominate the industry, not just because of their prevalence but because of how they’re perceived. Standard American, Australian, and British accents are often favored for their clarity, global reach, and perceived association with professionalism or prestige. Meanwhile, accents tied to specific regions such as France or India carry strong cultural identities, making them ideal for brands looking to evoke a particular mood or authenticity.
The Most Searched Celebrity AI Voices - AHrefs Data
Celebrity voice cloning remains one of the most popular applications of AI-generated speech, with certain figures dominating search trends. Donald Trump is the most frequently searched AI-generated voice, followed by David Attenborough and Morgan Freeman.
Celebrity voices are sought after because they carry immediate recognition. Trump’s presence at the top of the list is unsurprising given how frequently his voice is used in AI-generated political satire and social media content. Morgan Freeman’s deep, steady narration evokes trust and authority, making him a go-to for documentaries and commercials. These voices are in high demand because they instantly shape the perception of a message, adding credibility and emotional depth.
How Do AI Voices Work?
AI-generated voices have advanced far beyond the robotic-sounding speech of early experiments. Today, they can replicate human intonation, emotion, and nuance with impressive accuracy. But to get to where we are now, it has taken the industry nearly a century of trial and error.
The Evolution of AI Voice Synthesis
The earliest attempts at synthetic speech date back over 80 years. Bell Labs’ Voder (1939) produced crude, speech-like sounds through manual control. In the 1950s and 60s, systems like Audrey (1952) and IBM’s Shoebox (1962) introduced early speech recognition, but they could only understand single words or basic commands.
By the 1970s, the Hidden Markov Model (HMM) allowed speech recognition to work with probability-based predictions rather than simple pattern matching. This breakthrough made AI-generated speech more flexible, enabling machines to adapt to different voices and accents.
In 1997, Dragon NaturallySpeaking marked a turning point in speech recognition. Unlike earlier systems that required users to pause between words, it introduced continuous speech recognition, allowing natural, fluid dictation. This software became a foundation for future advancements in voice AI, proving that speech-to-text technology could be commercially viable and widely adopted.
However, the real shift happened in the 2010s with the rise of deep learning. Neural networks, large language models (LLMs), and text-to-speech (TTS) technology transformed AI-generated voices from stiff and mechanical to near-indistinguishable from real human speech. This is when AI voice assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant started to emerge and become the familiar voices we know and hear today.
The Introduction of AI Voice Cloning
More recently, AI voice cloning has been commercialized as a separate development from standard AI-generated voices. Instead of relying on pre-trained synthetic voices, voice cloning technology replicates a specific person’s voice with high accuracy. By training on recorded speech samples, AI can mimic tone, pitch, and unique vocal characteristics, making the cloned voice nearly indistinguishable from the original speaker.
The process typically involves deep learning models that analyze speech patterns, phonetics, and intonations to generate a digital voice clone. While early versions of this technology required hours of audio training data, modern systems can create a convincing clone with just a few minutes of recorded speech.
Voice cloning has significant implications. It allows voice actors to license an AI version of themselves, and for content creators to automate voiceovers while maintaining a consistent personal brand. For accessibility, it can even enable those with speech impairments to restore their natural voices using AI.
How AI Voice Technology Works
Modern AI voices are built using three key technologies:
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) Conversion: AI voices begin with raw text input. A TTS system breaks this down into phonemes, the smallest units of sound in language, and applies linguistic rules to determine pronunciation, rhythm, and emphasis.
- Neural Network Training: To generate realistic speech, AI models are trained on vast datasets of human voices. These datasets include different accents, tones, and speech styles. Through deep learning, the AI refines its ability to produce natural-sounding speech.
- Voice Cloning and Speech Synthesis: AI voice cloning takes this a step further. Instead of using a generic voice model, AI can replicate a specific person’s voice using a limited amount of recorded speech. Advanced systems can generate entirely new sentences in that person’s voice while preserving tone and emotion.
AI Voice Copyright Laws
AI-generated voices cannot be copyrighted under US law since copyright requires human authorship. While content featuring an AI-generated voice can be copyrighted, the voice itself remains unprotected. Instead, AI voice providers retain ownership through licensing agreements, meaning users can generate content but don’t own the voices. Providers can also set restrictions, modify, or remove voices at any time.
On the other hand, if you clone your own voice using a tool like Podcastle’s voice cloning, you own the recordings and AI-generated output, but not the underlying AI model. This means your cloned voice can’t be used outside the platform without your permission. Using AI-generated voices to imitate real people without consent, especially celebrities, can also violate likeness rights and lead to legal issues.
How to Tell AI Voices and Human Speech Apart
Just a few years ago, synthetic speech was easy to recognize, as it often sounded choppy, monotone, and lacking the natural flow of human conversation. Nowadays, survey data from Podcastle finds that 63% of Americans are unable to tell human and AI-generated voices apart.
With AI-generated voices becoming more and more indistinguishable from human speech, the need for detection tools is growing. Several companies have developed systems to analyze speech patterns and identify synthetic audio. Resemble Detect, ElevenLabs’ AI Speech Classifier, Deeptrace, and Reality Defender are among some of the leading AI voice detection tools in 2025, each using different methods to distinguish real voices from artificial ones. Some rely on spectrogram analysis to detect irregularities in sound waves, while others use acoustic fingerprinting to flag suspicious patterns in pitch and cadence.
However, while most of these AI detectors claim a 90% accuracy in detecting AI voices, NPR’s research tells a different story. After testing 84 audio clips, half real and half AI-generated, some tools misidentified nearly 50% of them, with others returning inconclusive results for a third of the samples.
Clearly, spotting AI isn’t as simple as these tools make it seem. Even with these advancements, AI voice detection is an ongoing challenge. As synthetic voices continue to improve, the gap between real and artificial will only get smaller, forcing industries, regulators, and creators to adapt to a world where hearing isn’t always believing.
Can You Spot the Difference?
Just to put things to the test, we recorded the same sentence said by a human and by an AI voice clone. Let's see if you can spot the difference, cast your vote in the poll below! (If you want to check if you're right, the answer is near the bottom of this page.)
The Ethics of AI Voices and Voice Cloning
The rise of AI-generated voices has opened up a world of possibilities, but it has also raised urgent ethical questions. Who owns an AI-generated replica of a real person’s voice? What happens when someone’s voice is cloned without their consent? These concerns are currently playing out in real-world legal battles and industry debates.
Celebrities have been among the first to experience the risks. Podcastle research found that Arnold Schwarzenegger, Donald Trump, Kim Kardashian, and Sylvester Stallone are some of the most vulnerable to AI voice cloning misuse. Schwarzenegger topped the list, with 86% of Americans saying his accent is easy to replicate.
High-profile figures aren’t the only ones at risk. Even TikTok’s text-to-speech feature landed in legal trouble when voice actor Beverly Standing sued ByteDance in 2021 for using her voice without permission. The case underscored how easy it is for companies to deploy AI-generated voices without compensating or even informing the original voice owners. More recently, Scarlett Johansson took action against OpenAI after discovering that a voice eerily similar to hers was used in their previous model without her authorization.
Regulations are starting to take shape, but progress is slow. Several US states have proposed or enacted laws restricting AI-generated deepfake content, such as California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). The EU’s AI Act also includes provisions for identifying and regulating synthetic voices. But without a standardized global framework, enforcing these policies remains a challenge, and as AI voices become more advanced, more creators, businesses, and policymakers will need to address the balance between innovation and consent.
How Clients Choose Voiceover Artists
With AI voices becoming an affordable alternative, companies are rethinking how they find and hire voice talent. Some still turn to traditional platforms, agencies, or freelance networks, but others are weighing the cost and flexibility of AI-generated narration. This shift has made voice actors more conscious of what sets them apart: versatility, emotional depth, and the ability to adapt to a brand’s message.
Where Clients Find Voice Talent
Clients use different methods to source voiceover artists, depending on their project’s budget, urgency, and quality expectations:
- Voiceover Marketplaces: Platforms like Voice123 and Voices.com allow businesses to quickly browse, compare, and book voice actors. These platforms are specifically tailored for voiceover artists and opportunities.
- Freelance Marketplaces: Sites like Fiverr and Upwork provide more budget-friendly options but often require clients to sift through more entry-level talent.
- Direct Outreach & Networking: Established voice actors often secure work through word-of-mouth referrals, LinkedIn networking, or personal websites with demo reels.
- Talent Agencies: Major brands, AAA game studios, and national ad campaigns rely on agencies to source vetted professionals. Agencies handle negotiations, contracts, and guarantee the talent delivers high-quality work ready for broadcast.
Key Voice Actor Hiring Considerations
A strong voice can amplify any project, but hiring the right actor requires a thorough look at their background and their ability to adapt to different styles and audiences. Before making a choice, these are the key factors companies consider to determine if the voice fits their message.
1) Experience and Versatility
Clients look for voice actors with a track record of delivering quality work across different formats: commercials, narration, animation, and more. Those with formal training or coaching tend to have an additional advantage, as it’s often a marker for better tone, pacing, and character work, making them a safer choice for complex projects.
2) Clarity, Pacing, and Emotional Depth
A clear voice keeps the message sharp, but delivery matters just as much. The right pacing makes a script flow naturally, while emotional depth gives the performance authenticity. A voice that feels robotic or flat can turn a great script into a forgettable one.
3) Professionalism and Dependability
Deadlines, revisions, and consistency all play a role in a smooth production. Voice actors whose profiles showcase recommendations from past clients and proven reliability are much more likely to secure ongoing work and land high-value projects.
4) Cultural Awareness and Adaptability
Great voice actors immerse themselves deeply in the cultures they portray. They grasp subtle references that scripts won’t explicitly mention but audiences immediately sense. Truly connecting with listeners means knowing what makes them laugh, what touches their hearts, or even what might offend them.
5) Pricing and Budget Fit
Clients evaluate pricing based on the scope of the project, any licensing terms, and the level of experience required. Weighing these factors helps determine whether a voice actor’s rate aligns with the value they bring to the project.
The Future of AI and Human Voiceovers
AI voices are evolving, and in many cases becoming indistinguishable, but they still struggle with nuance. Yelling, whispering, sarcasm, and deep emotion remain difficult to replicate. This bodes well for voice actors, who can focus on creative, high-value work rather than routine, practical gigs. Instead of replacing them, AI is opening up new opportunities by shifting the focus to more expressive performances, and it’s why 66% of creatives believe that AI will actually create more job opportunities rather than take them away.
However, AI voices will keep improving, and with this trajectory in mind, the voice actors who will thrive long-term will likely be those who integrate AI into their careers. Many are already licensing their voices to AI companies, turning training data into passive income. Others use AI-generated voices for quick, entry-level work while dedicating their time to complex projects that require human skill. This balance lets them target more work in less time, making the industry more efficient rather than more competitive.
How To Create Content with AI Voices
AI-generated voices can be powerful tools for content creation, but using them effectively requires some guidelines. Here’s how to make the most of AI voice technology while keeping content engaging and professional.
1) Mix AI and Real Voices
AI voices can handle quick edits, script drafts, or filler content, but they lack the emotional nuance of human voice actors. Use AI where efficiency matters, but rely on real voices for moments that need authenticity and depth.
2) Experiment with Different Tones
Test various AI voice styles, whether it’s serious, playful, or conversational, to find what resonates best with your audience. Small adjustments can make a big difference in how natural the final audio sounds.
3) Polish Every Track
Raw AI-generated audio often sounds mechanical. Sometimes, something as simple as punctuation can change the way AI sounds. For deeper work, editing tools like EQ adjustments, noise reduction, and pacing tweaks can help smooth things out.
4) Be Transparent with Your Audience
If you’re using AI-generated voices, let your audience know. Transparency builds trust, and many viewers appreciate the efficiency of AI while still valuing human creativity. A simple note in your content description or credits can go a long way.
5) Pair AI Voices with Strong Visuals
A compelling voiceover works best alongside engaging visuals. So if you’re working on video content, animations, or slideshows, combining AI voices with dynamic imagery enhances the overall impact and keeps audiences engaged.
Where Do We Go From Here?
The rise of AI voice technology has sparked widespread concern about the future of the voiceover industry. Many fear that human voice actors will be replaced, that jobs will disappear, and that AI-generated voices will dominate the space. But the reality is far from that.
The data tells a different story: AI voices aren’t eliminating opportunities, they’re expanding them. The surge in content creation means more demand for voiceovers than ever before, and AI technology has made high-quality audio accessible to creators who previously couldn’t afford it. Instead of replacing human voice actors, AI is shifting the industry’s focus. Routine voice work can now be automated, freeing up professionals to take on more dynamic, emotionally rich projects that require real human depth.
What is true is that AI voices are changing the way the industry works. Voice actors now have more room to explore high-impact storytelling, unique character work, and premium creative projects where AI simply can’t compete. And for businesses and independent creators, AI voices open new doors, making professional-grade audio production faster, more flexible, and more cost-effective.
At Podcastle, we believe AI and human creativity go hand in hand. Try Podcastle’s AI voices for free and see how technology can enhance your storytelling without replacing the artistry that makes voiceover work so powerful.
AdRead Answers:
We thought it would be interesting to see if you could tell the difference between a human and an AI ad read. The twist? Both were AI-generated. Did you catch the trick, or did we manage to surprise you?
Voice Cloning:
– Voice 1: AI
– Voice 2: Human
References
- https://straitsresearch.com/report/ai-voice-generators-market
- https://elevenlabs.io/blog/series-c
- https://podcastle.ai/announcements/podcastle-series-a-funding-announcement/
- https://deepgram.com/learn/state-of-voice-2023-report
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/virginieberger/2024/08/21/sag-aftras-ai-deal-a-5-billion-gamble-on-the-future-of-voice-acting/
- https://www.demandsage.com/spotify-stats/
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/podcast-market
- https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/industry-reports/audiobooks-market
- https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/video-game-market
- https://www.agilitypr.com/pr-news/public-relations/the-power-of-video-93-percent-of-brands-landed-a-new-customer-after-sharing-one-on-social-media/
- https://www.theguardian.com/technology/article/2024/jun/30/ai-clones-voice-acting-industry-impact-australia
- https://www.voices.com/company/press/reports/2022-state-of-voice-over
- https://podcastle.ai/blog/future-of-voice/
- https://www.npr.org/2024/04/05/1241446778/deepfake-audio-detection
- https://podcastle.ai/blog/celebrity-ai-voices/
- https://www.theguardian.com/technology/article/2024/may/27/scarlett-johansson-openai-legal-artificial-intelligence-chatgpt
- https://www.nationalsecuritylawfirm.com/understanding-voice-cloning-the-laws-and-your-rights/
- https://www.onetrust.com/blog/navigating-the-eu-ai-act/
- https://www.voices.com/company/press/reports/ai-in-the-creative-industry










