Cleaning up the audio from a student interview. Transcribing a two-hour focus group. Switching camera angles in a recorded class debate. Re-recording a voiceover because one line in the slide deck changed. None of it is difficult, but it adds up fast.
Those kinds of tasks eat into time that’s already stretched thin. But skipping them makes the material harder to use later. It’s harder to share, harder to study, harder to turn into something better.
AI can take care of those jobs without getting in the way. It can fix audio without needing another take. It can generate transcripts as soon as a session ends. It can pick the right speaker view without manual editing. It can read a new script out loud so you don’t have to re-record anything.
Not every problem needs a new tool. But when the work keeps stacking up, small things like this make a difference.
How AI Benefits Education
1. Full transcripts without wasting half your day
Typing out a roundtable discussion takes hours. Even if you use a standard transcription tool, you usually have to fix names, punctuation, speaker labels, and awkward phrasing. AI transcription handles all of it in minutes. It identifies who’s speaking, gets the flow right, and gives you something clean enough to share or quote right away.
It’s especially useful after long group sessions, guest lectures, or recorded lessons where reviewing the material matters just as much as delivering it.
2. Audio cleanup that actually works
You don’t always get a quiet room. Some student recordings come in with background chatter. Guest speakers call in with bad mics. Group discussions are recorded in noisy halls. AI audio tools can fix all of that, removing hums, boosting clarity, balancing volume, without making everything sound robotic.
It’s the kind of fix that used to mean re-recording, or just putting up with bad sound. Now it’s something you can do in a few clicks and move on.
3. Clearer video interviews without editing for hours
Let’s say you’ve recorded a discussion between three students. You want to show it in class or clip it for review, but it’s hard to follow because the camera stays on the wrong person half the time. AI video tools can automatically switch between speakers, center each shot, and make the layout easier to follow without opening an editing timeline or cutting a single frame by hand.
It’s especially helpful when recording interviews, presentations, or student-led projects where multiple people are speaking.
4. Video that looks sharper, more focused, and easier to follow
If you’re recording lessons, presentations, or group discussions using a basic webcam, the video often comes out flat. AI video tools can sharpen the footage with upscaling, so it looks clearer even if it was recorded in low resolution. They can also blur the background slightly to bring focus to the speaker, especially helpful when recording from home or a shared space.
Some tools even correct eye contact, adjusting your gaze so it looks like you’re speaking directly to the viewer. That small shift makes a big difference when someone’s watching a recorded lesson or explainer video, it helps hold their attention and makes the material feel more personal, even after the fact.
5. Voiceovers without recording a thing
You finish building a video lesson, but one part of the script changes. Or maybe there’s no time to record a voiceover at all. Instead of delaying or recording in a rush, AI voice tools can read your script in a natural voice and fill the gap.
This works well for quick edits, explainer videos, or any educational content where the visuals are ready but the audio needs to catch up. It’s not a replacement for live teaching, it’s a practical fix when you just need the words delivered clearly.
6. Repurposing content without starting from scratch
A single recording, like a guest lecture or student presentation, can be turned into multiple formats. The full session becomes a transcript. Key moments become short clips. A quick summary becomes voiceover for a slide deck. AI makes that process faster by handling the technical steps: cutting clips, cleaning up audio, generating text, and producing clean exports.
This makes it easier to reuse existing material for different contexts, like sharing a summary with one group, reviewing the full version with another, or turning part of it into a resource for the next term.
7. Smarter AI generated summaries
Long documents can take a while to sift through. Sometimes you just need the key points, what was said, what it means, what to do with it. Tools like NotebookLM can read through the content and pull out useful summaries, questions, or suggestions based on the material.
This helps when preparing to teach from complex readings, reviewing long papers, or breaking down research for others. It doesn’t replace the deep work, but it gets you to the starting line faster.
8. Notes that write themselves
Trying to take notes during a live discussion always means missing something. You either fall behind or tune out while writing. AI note-taking tools record everything, transcribe it in real time, and highlight key moments automatically.
That’s useful in any setting where people are speaking freely, classroom discussions, interviews, group projects, or panels. You can go back and review what was said, pull quotes, or skim the highlights without needing to rewatch the whole session. It frees up focus during the moment without losing anything important.
9. Generative AI that helps plan, explain, and revise
Tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Deepseek can help break down complex topics, brainstorm activity ideas, or rewrite confusing instructions. They’re used to summarize readings, simplify difficult concepts, suggest quiz questions, or draft rubrics. In research-heavy settings, they can help outline essays or clarify how different sources connect.
These tools don’t replace the thinking, but they’re useful when you’re stuck, short on time, or trying to turn raw ideas into something more structured. Like any resource, the output needs to be checked and shaped. But it’s a fast way to get moving when you’re staring at a blank page.
10. Accessibility features that help everyone
Not all students process content the same way. Some need captions. Some need transcripts. Some need audio versions of written material. AI makes it easier to create all of those things automatically, without extra production time.
You can take a recorded discussion and get a full transcript with speaker names. You can add subtitles to a video in seconds. You can turn text into audio so it’s easier to absorb on the go. These aren’t extras, they’re tools that help make the material available to more people, in more ways.
How to use AI for Education with Podcastle
Transcribing an interview. Adding voiceover to a video lesson. Cleaning up audio from a group discussion. These are the kinds of tasks that slow everything down. Here’s how to use Podcastle to get them done faster, with tools that are simple, accurate, and designed to save you time.
Step 1: Upload Your Recording or Start a Voice Project
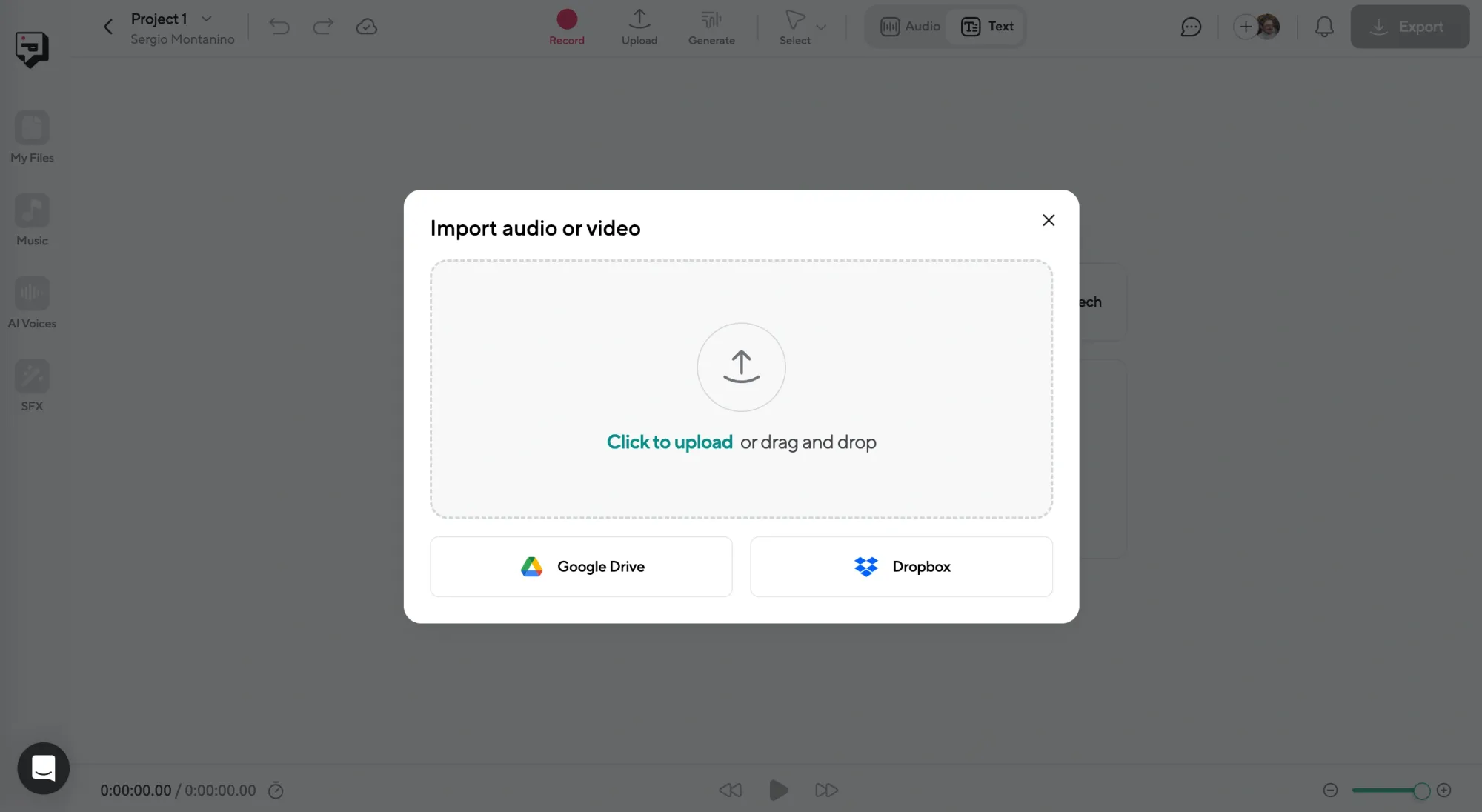
To transcribe an interview, start by uploading your audio or video file into Podcastle. Just drag and drop it into the dashboard. The same workspace also lets you begin a voiceover project from scratch if you’re working with a script instead of a recording.
👉 For interviews or group sessions, high-quality audio makes a big difference. Clear speech means fewer transcription errors later.
Step 2: Transcribe or Add Your Script
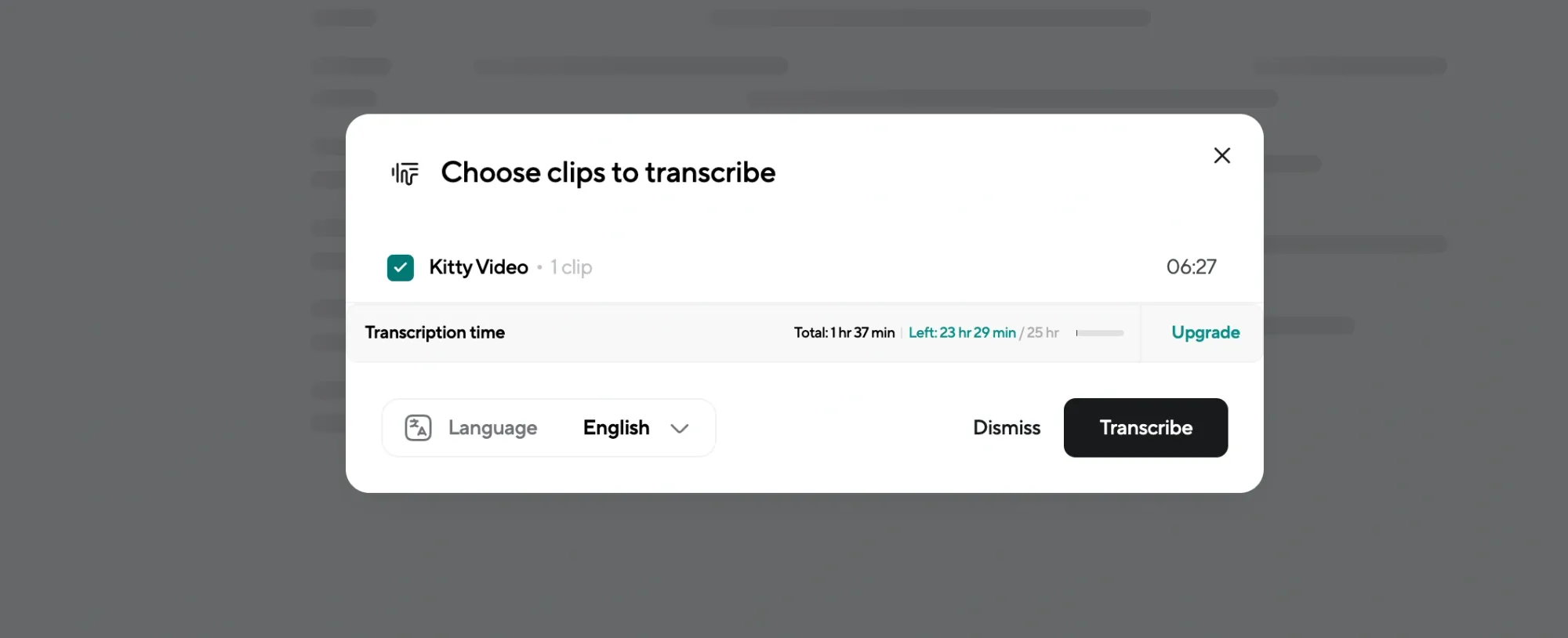
If you’re transcribing, click “Transcribe” and let the AI convert your audio into text automatically. It works for both solo recordings and multi-speaker sessions. The transcript appears in seconds, ready for review.
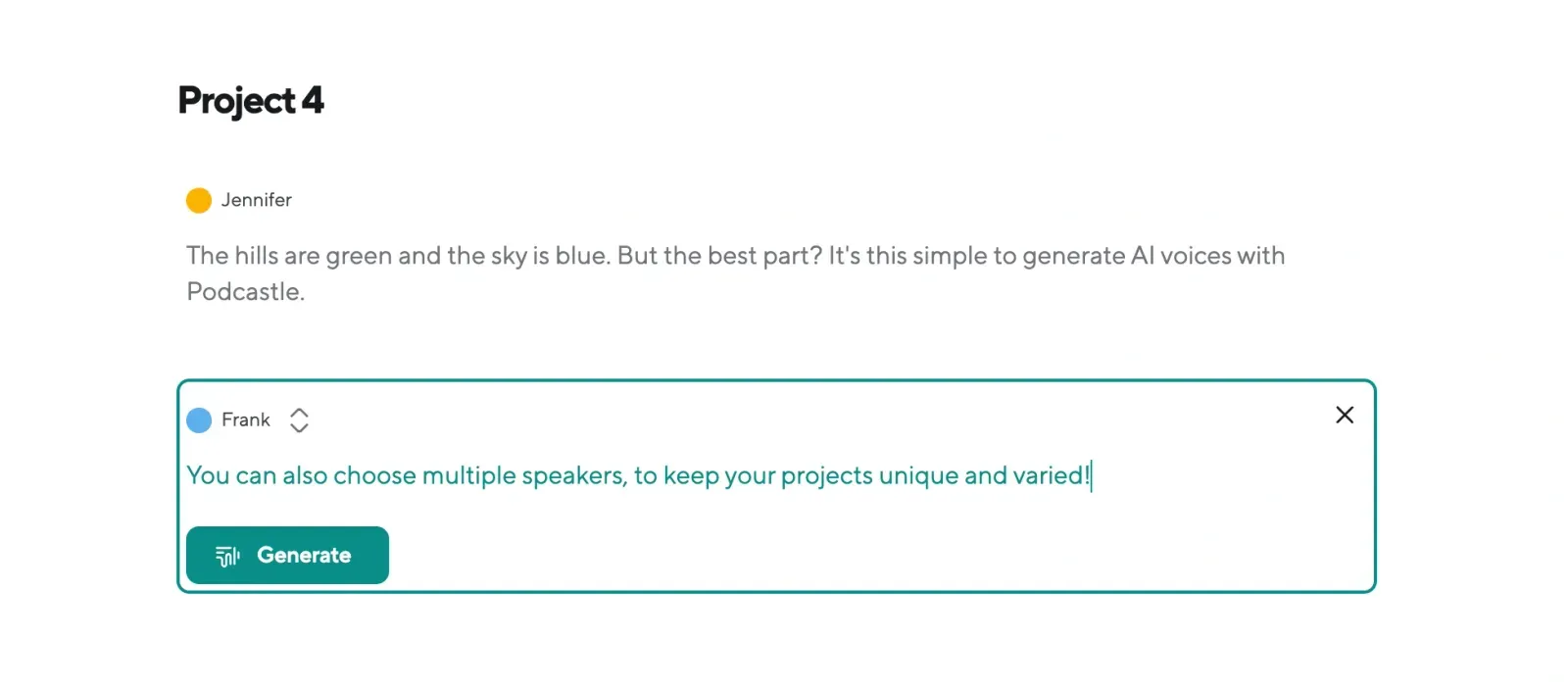
If you’re creating a voiceover, choose “AI Voices” instead. Paste your script into the editor and browse the voice library. There are accents and tones for different formats, presentations, storytelling, or more formal content.
Step 3: Review, Edit, and Customize
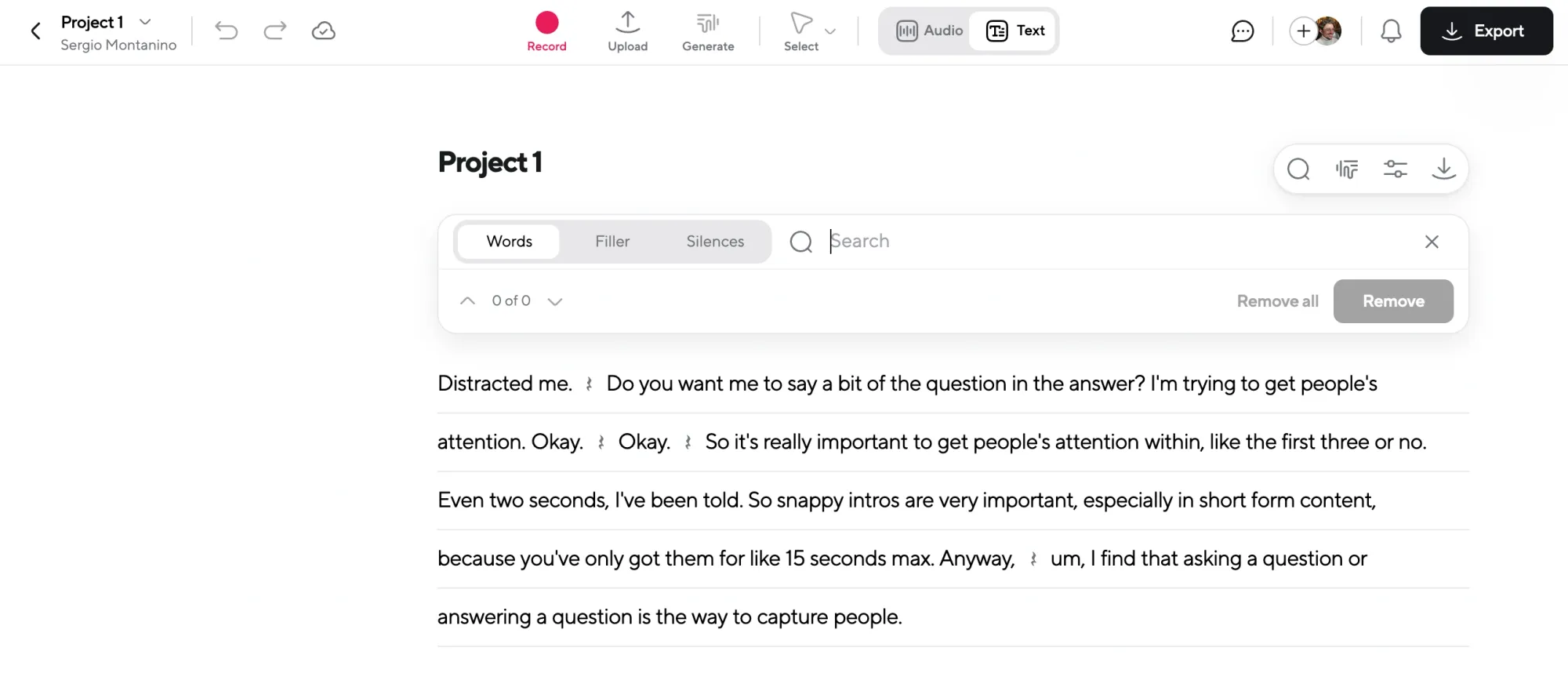
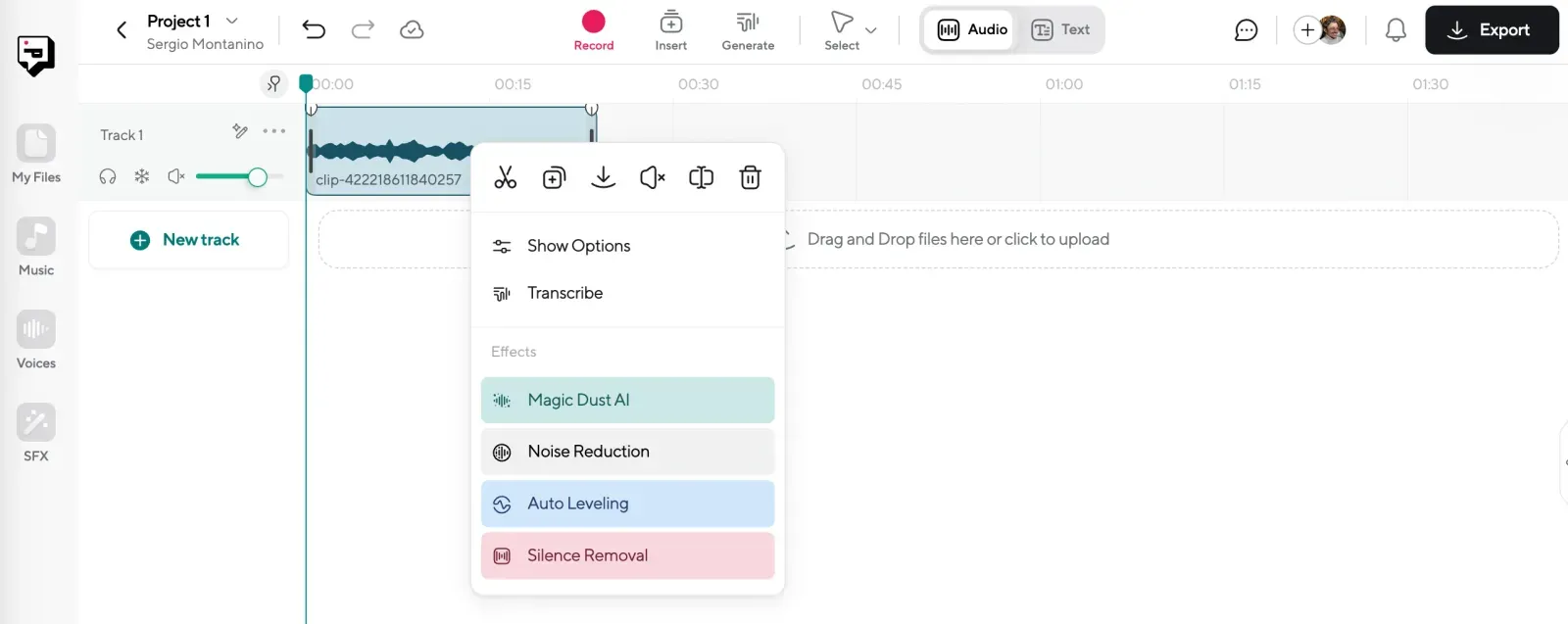
For transcripts, proofread the text directly in the editor. You can fix any misheard words, adjust punctuation, and double-check speaker labels. The editing feels like working in a doc, simple and fast.
For voiceovers, this is where you refine the delivery. Adjust pacing, fix pronunciation, and use punctuation to shape the tone. You can also apply effects like Magic Dust to clean up the audio and make it sound more natural.
👉 Speaker detection helps identify who’s talking in a multi-voice interview. For voiceovers, you can even assign different AI voices to different parts of the script if you’re recreating a dialogue or group setting.
Step 4: Export Your Work
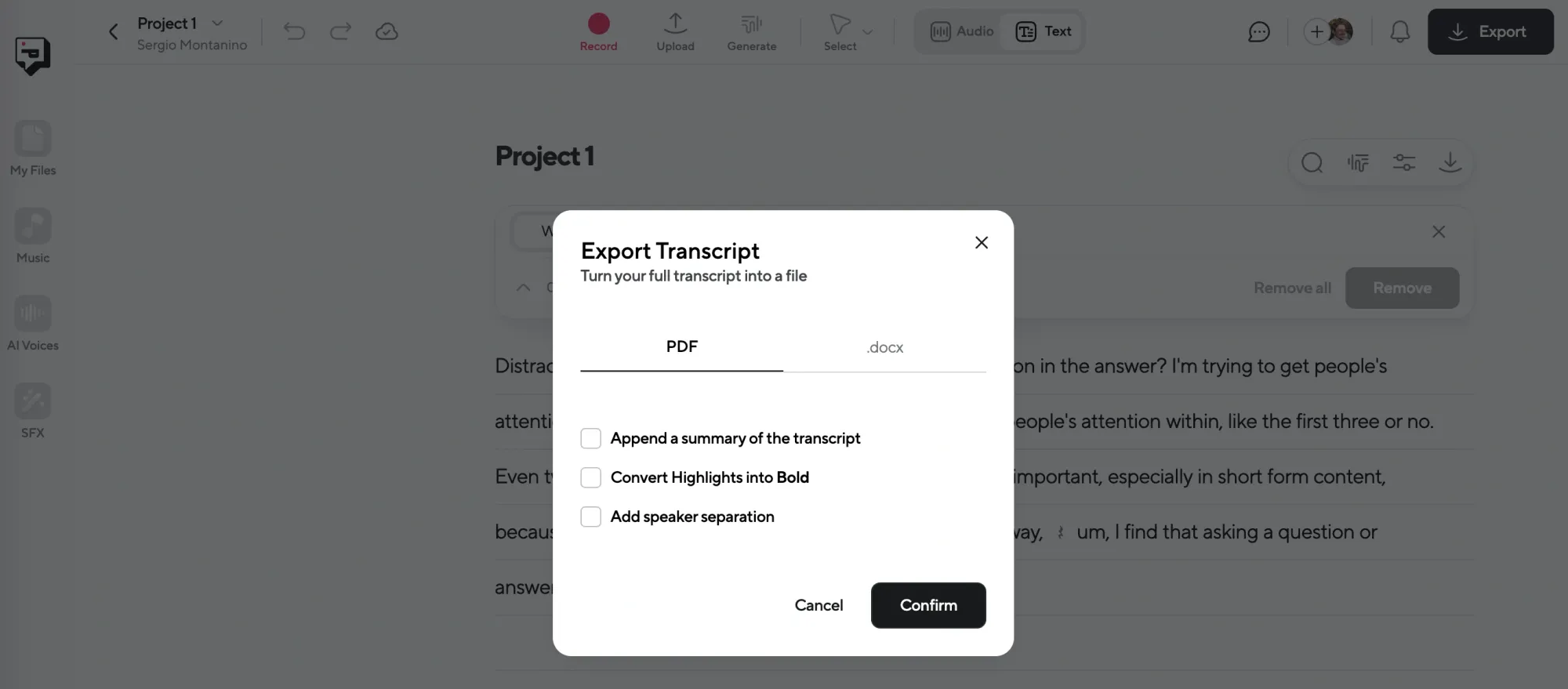
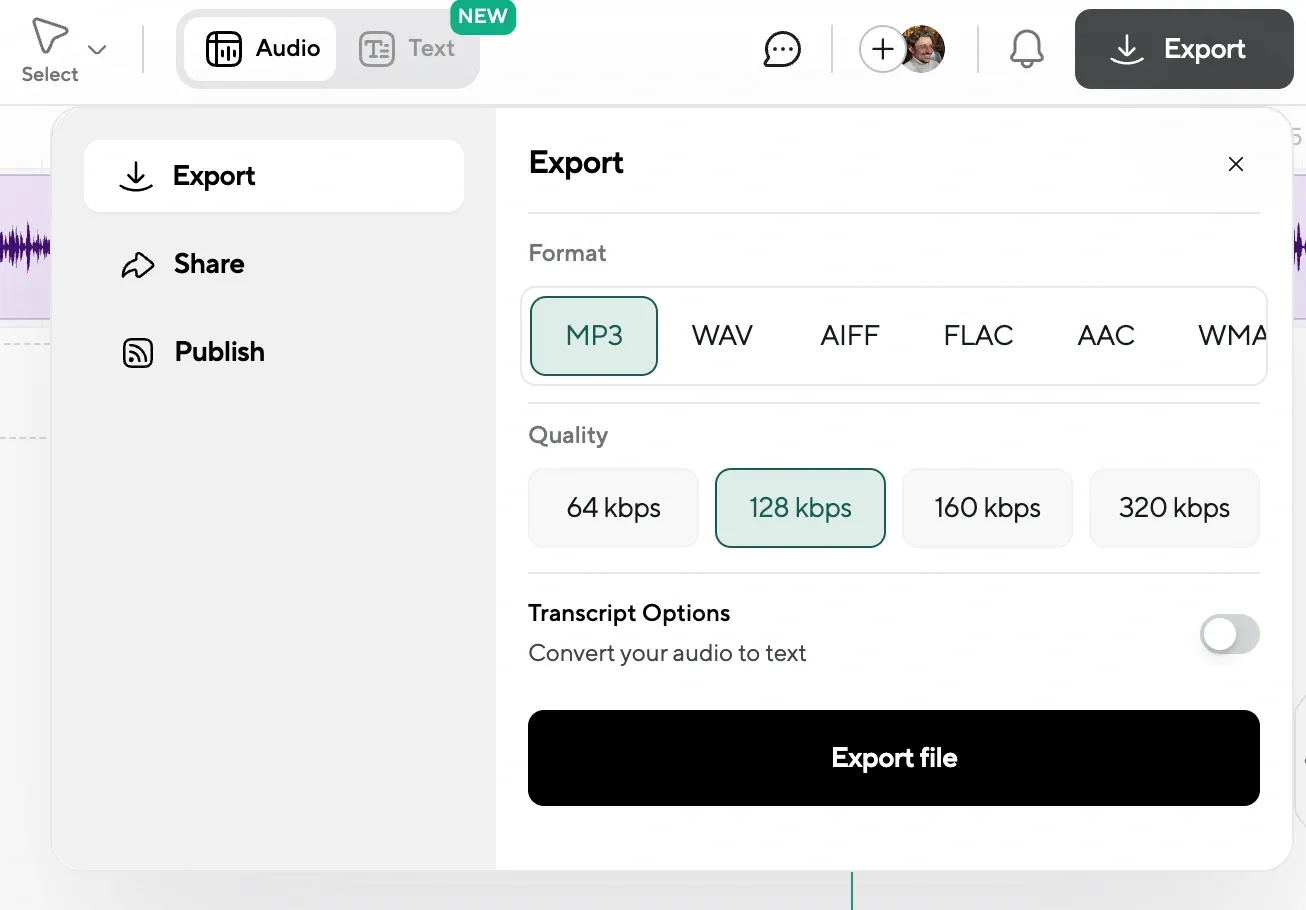
Once everything looks and sounds right, export the final file. Transcripts can be downloaded as TXT, DOCX, or SRT (for subtitles). Audio can be saved in MP3 or WAV format.
At this point, you can use the transcript in a blog post, report, or paper, or pair it with your video for captions. The voiceover can be added to a slide deck, turned into a standalone audio lesson, or layered with music and effects for a podcast-style piece.
Final Thoughts
The work behind educational content doesn’t stop when the recording ends. Transcripts need cleaning. Audio needs fixing. Scripts need updating. That work takes time, but it doesn’t have to take all of it.
AI tools aren’t here to replace anything important. They’re here to make the small, necessary tasks easier to manage. The parts you’d normally put off. The things that slow you down when you’re already stretched thin.
Used well, they help you keep up without cutting corners. And when the basics are handled, there’s more space to focus on what actually matters, explaining clearly, sharing ideas, and building material people can use.